Overview
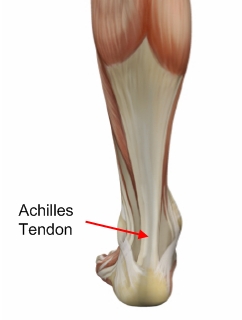
The Achilles tendon is an important part of the leg. It is located just behind and above the heel. It joins the heel bone to the calf muscles. Its function is to help in bending the foot downwards at the ankle (this movement is called plantar flexion by doctors). If the Achilles tendon is torn, this is called an Achilles tendon rupture. The tear may be either partial or complete. In a partial tear, the tendon is partly torn but still joined to the calf muscle. With complete tears, the tendon is completely torn so that the connection between the calf muscles and the ankle bone is lost.
Causes
Achilles tendon rupture occurs in people that engage in strenuous activity, who are usually sedentary and have weakened tendons, or in people who have had previous chronic injury to their Achilles tendons. Previous injury to the tendon can be caused by overuse, improper stretching habits, worn-out or improperly fitting shoes, or poor biomechanics (flat-feet). The risk of tendon rupture is also increased with the use of quinolone antibiotics (e.g. ciprofloxacin, Levaquin).
Symptoms
The pain from an Achilles tendon rupture is usually felt in the back of the lower leg, in the area 2 to 6 cm. above the Achilles tendon's attachment to the calcaneus. Individuals with an Achilles tendon rupture often describe a "pop" or similar feeling at the time of the injury. A "hole" or defect in the Achilles tendon can usually be felt under the skin in this area. A limp and inability to rise up on the toes of the affected foot are usually present. If the affected foot does not plantar flex when the calf muscles are squeezed an Achilles tendon rupture is very likely.
Diagnosis
Your caregiver will ask what you were doing at the time of your injury. You may need any of the following. A calf-squeeze test is used to check for movement. You will lie on your stomach on a table or bed with your feet hanging over the edge. Your caregiver will squeeze the lower part of each calf. If your foot or ankle do not move, the tendon is torn. An x-ray will show swelling or any broken bones. An ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures of your tendon on a monitor. An ultrasound may show a tear in the tendon. An MRI takes pictures of your tendon to show damage. You may be given dye to help the tendon show up better. Tell the caregiver if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast dye. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the caregiver if you have any metal in or on your body.
Non Surgical Treatment
As debilitating as they can be, the good news is that minor to moderate Achilles tendon injuries should heal on their own. You just need to give them time. To speed the healing, you can try the following. Rest your leg. Avoid putting weight on your leg as best you can. You may need crutches. Ice your leg. To reduce pain and swelling, ice your injury for 20 to 30 minutes, every three to four hours for two to three days, or until the pain is gone. Compress your leg. Use an elastic bandage around the lower leg and ankle to keep down swelling. Elevate your leg. Prop you leg up on a pillow when you're sitting or lying down. Take anti-inflammatory painkillers. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve) will help with pain and swelling. However, these drugs have side effects, such as an increased risk of bleeding and ulcers. They should be used only occasionally unless your health care provider says otherwise and should be taken with food. Check with your doctor before taking these if you have any allergies, medical problems or take any other medication. Use a heel lift. Your health care provider may recommend that you wear an insert in your shoe while you recover. It will help protect your Achilles tendon from further stretching. Practice stretching and strengthening exercises as recommended by your health care provider. Usually, these techniques will do the trick. But in severe cases of Achilles tendon injury, you may need a cast for six to 10 weeks or even surgery to repair the tendon or remove excess tissue.

Surgical Treatment
Debate remains regarding the best form of treatment for a ruptured Achilles tendon. The 2 options are:immobilisation or operation. A recent meta-analysis of scientific studies showed that compared to immobilisation, an operation reduces the risk of re-rupture and allows a quicker return to work. An operation is not without risk and these must be balanced against the benefit of a lower re-rupture rate. Both treatments involve immobilisation for 8 weeks.
Prevention
Here are some suggestions to help to prevent this injury. Corticosteroid medication such as prednisolone, should be used carefully and the dose should be reduced if possible. But note that there are many conditions where corticosteroid medication is important or lifesaving. Quinolone antibiotics should be used carefully in people aged over 60 or who are taking steroids.

The Achilles tendon is an important part of the leg. It is located just behind and above the heel. It joins the heel bone to the calf muscles. Its function is to help in bending the foot downwards at the ankle (this movement is called plantar flexion by doctors). If the Achilles tendon is torn, this is called an Achilles tendon rupture. The tear may be either partial or complete. In a partial tear, the tendon is partly torn but still joined to the calf muscle. With complete tears, the tendon is completely torn so that the connection between the calf muscles and the ankle bone is lost.
Causes
Achilles tendon rupture occurs in people that engage in strenuous activity, who are usually sedentary and have weakened tendons, or in people who have had previous chronic injury to their Achilles tendons. Previous injury to the tendon can be caused by overuse, improper stretching habits, worn-out or improperly fitting shoes, or poor biomechanics (flat-feet). The risk of tendon rupture is also increased with the use of quinolone antibiotics (e.g. ciprofloxacin, Levaquin).
Symptoms
The pain from an Achilles tendon rupture is usually felt in the back of the lower leg, in the area 2 to 6 cm. above the Achilles tendon's attachment to the calcaneus. Individuals with an Achilles tendon rupture often describe a "pop" or similar feeling at the time of the injury. A "hole" or defect in the Achilles tendon can usually be felt under the skin in this area. A limp and inability to rise up on the toes of the affected foot are usually present. If the affected foot does not plantar flex when the calf muscles are squeezed an Achilles tendon rupture is very likely.
Diagnosis
Your caregiver will ask what you were doing at the time of your injury. You may need any of the following. A calf-squeeze test is used to check for movement. You will lie on your stomach on a table or bed with your feet hanging over the edge. Your caregiver will squeeze the lower part of each calf. If your foot or ankle do not move, the tendon is torn. An x-ray will show swelling or any broken bones. An ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures of your tendon on a monitor. An ultrasound may show a tear in the tendon. An MRI takes pictures of your tendon to show damage. You may be given dye to help the tendon show up better. Tell the caregiver if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast dye. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the caregiver if you have any metal in or on your body.
Non Surgical Treatment
As debilitating as they can be, the good news is that minor to moderate Achilles tendon injuries should heal on their own. You just need to give them time. To speed the healing, you can try the following. Rest your leg. Avoid putting weight on your leg as best you can. You may need crutches. Ice your leg. To reduce pain and swelling, ice your injury for 20 to 30 minutes, every three to four hours for two to three days, or until the pain is gone. Compress your leg. Use an elastic bandage around the lower leg and ankle to keep down swelling. Elevate your leg. Prop you leg up on a pillow when you're sitting or lying down. Take anti-inflammatory painkillers. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) and naproxen (Aleve) will help with pain and swelling. However, these drugs have side effects, such as an increased risk of bleeding and ulcers. They should be used only occasionally unless your health care provider says otherwise and should be taken with food. Check with your doctor before taking these if you have any allergies, medical problems or take any other medication. Use a heel lift. Your health care provider may recommend that you wear an insert in your shoe while you recover. It will help protect your Achilles tendon from further stretching. Practice stretching and strengthening exercises as recommended by your health care provider. Usually, these techniques will do the trick. But in severe cases of Achilles tendon injury, you may need a cast for six to 10 weeks or even surgery to repair the tendon or remove excess tissue.

Surgical Treatment
Debate remains regarding the best form of treatment for a ruptured Achilles tendon. The 2 options are:immobilisation or operation. A recent meta-analysis of scientific studies showed that compared to immobilisation, an operation reduces the risk of re-rupture and allows a quicker return to work. An operation is not without risk and these must be balanced against the benefit of a lower re-rupture rate. Both treatments involve immobilisation for 8 weeks.
Prevention
Here are some suggestions to help to prevent this injury. Corticosteroid medication such as prednisolone, should be used carefully and the dose should be reduced if possible. But note that there are many conditions where corticosteroid medication is important or lifesaving. Quinolone antibiotics should be used carefully in people aged over 60 or who are taking steroids.
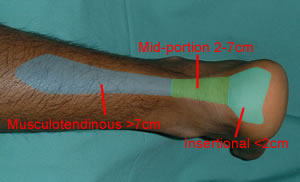
 Achilles Tendonitis is an inflammation of the Achilles Tendon. This tendon attaches the muscles in the calf of the leg to the back of our heels. The Achilles Tendon is a long and thick tendon, which moves our foot down, so that the toes point to the ground (plantar flexion). This tendon can become inflamed due to the following causes. Over utilizing it, such as too much running, especially up or down hill. Trauma, such as a kick to the tendon. Shoe or boot pressure, especially at its attachment to the heel, or just above it. There are over 250,000 injuries to the Achilles Tendon annually. In fact, more Than 10% of all running injuries are to the Achilles tendon. Tendonitis may be classified as either acute or chronic. Acute Achilles Tendonitis comes on quickly, usually after a specific activity or event. It is characterized by an overstretching or tearing of some of the small fibers of the tendon, and causes pain or tenderness when walking or running. It can occur at the insertion (near the attachment to the heel bone, or further up the leg, about 4 or 5 inches above the heel. Acute tendonitis can also follow a specific injury, such as a kick to the tendon while playing soccer. Chronic Achilles Tendonitis develops gradually over time. Many times, you can feel an obvious thickening of the tendon that may be tender when squeezed, due to long standing scarring of the tendon. Pain is also present when walking or during other forms of activity, and feels better at rest.
Achilles Tendonitis is an inflammation of the Achilles Tendon. This tendon attaches the muscles in the calf of the leg to the back of our heels. The Achilles Tendon is a long and thick tendon, which moves our foot down, so that the toes point to the ground (plantar flexion). This tendon can become inflamed due to the following causes. Over utilizing it, such as too much running, especially up or down hill. Trauma, such as a kick to the tendon. Shoe or boot pressure, especially at its attachment to the heel, or just above it. There are over 250,000 injuries to the Achilles Tendon annually. In fact, more Than 10% of all running injuries are to the Achilles tendon. Tendonitis may be classified as either acute or chronic. Acute Achilles Tendonitis comes on quickly, usually after a specific activity or event. It is characterized by an overstretching or tearing of some of the small fibers of the tendon, and causes pain or tenderness when walking or running. It can occur at the insertion (near the attachment to the heel bone, or further up the leg, about 4 or 5 inches above the heel. Acute tendonitis can also follow a specific injury, such as a kick to the tendon while playing soccer. Chronic Achilles Tendonitis develops gradually over time. Many times, you can feel an obvious thickening of the tendon that may be tender when squeezed, due to long standing scarring of the tendon. Pain is also present when walking or during other forms of activity, and feels better at rest.




 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
