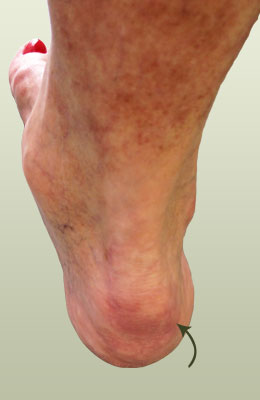
Overview
Bone spurs are bony projections that develop along the edges of bones. Bone spurs (osteophytes) often form where bones meet each other - in your joints. They can also form on the bones of your spine. The main cause of bone spurs is the joint damage associated with osteoarthritis. Most bone spurs cause no symptoms and may go undetected for years. They may not require treatment. Decisions about treatment depend on where spurs are situated and how they affect your health.
Causes
Heel spurs are exacerbated by an movements that stretch, twist or impact the plantar ligaments. Running, jumping, standing or walking on hard surfaces with unsupportive shoes, walking barefoot in sand are all activities that can activate heel spurs and plantar fasciitis. Obesity is another factor that increases stress to the plantar ligaments.

Symptoms
Most heel spurs cause no symptoms and may go undetected for years. If they cause no pain or discomfort, they require no treatment. Occasionally, a bone spur will break off from the larger bone, becoming a ?loose body?, floating in a joint or embedding itself in the lining of the joint. This can cause pain and intermittent locking of the joint. In the case of heel spurs, sharp pain and discomfort is felt on the bottom of the foot or heel.
Diagnosis
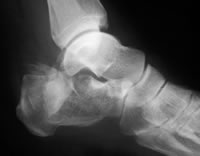
A heel spur is often seen on X-ray as a bony protrusion, which can vary in size. However, because a Heel Spur only indicates increased load on the plantar fascia, and not pain, an ultra sound may be required to assess other actual cause of the heel pain such and may include checking to see if the plantar fascia is inflamed or degenerated.
Non Surgical Treatment
Many treatment options exist, and good results are often observed. Generally, a calcaneal spur develops when proper care is not given to the foot and heels. It is often seen as a repetitive stress injury, and thus lifestyle modification is typically the basic course of management strategies. To alleviate heel spur pain, a person should begin doing foot and calf workouts. Strong muscles in the calves and lower legs will help take the stress off the bone and thus help cure or prevent heel spurs. Icing the area is an effective way to get immediate pain relief.
Surgical Treatment
Most studies indicate that 95% of those afflicted with heel spurs are able to relieve their heel pain with nonsurgical treatments. If you are one of the few people whose symptoms don?t improve with other treatments, your doctor may recommend plantar fascia release surgery. Plantar fascia release involves cutting part of the plantar fascia ligament in order to release the tension and relieve the inflammation of the ligament. Sometimes the bone spur is also removed, if there is a large spur (remember that the bone spur is rarely a cause of pain. Overall, the success rate of surgical release is 70 to 90 percent in patients with heel spurs. One should always be sure to understand all the risks associated with any surgery they are considering.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
